Advanced Persistent Threat
APT: A bit of history
- The earliest published attack on military research establishments was detected as far back as the late 1980s when West German hackers penetrated networked computers in California to steal secrets relating to the “Star Wars” program.
- A fascinating account of this particular set of attacks is related in the 1989 book The Cuckoo’s Egg: Tracking a Spy Through the Maze of Computer Espionage, by Clifford Stoll, a computer manager at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, who stumbled across the activity when investigating a minor accounting discrepancy in the computer usage accounts.
- Titan Rain was the code name given by the U.S. government to a series of cyber espionage attacks launched in 2003 on U.S. defense contractors, including those at Lockheed Martin, Sandia National Laboratories, Redstone Arsenal and NASA. The attacks were claimed to be of Chinese origin, although the Chinese government denied any involvement.
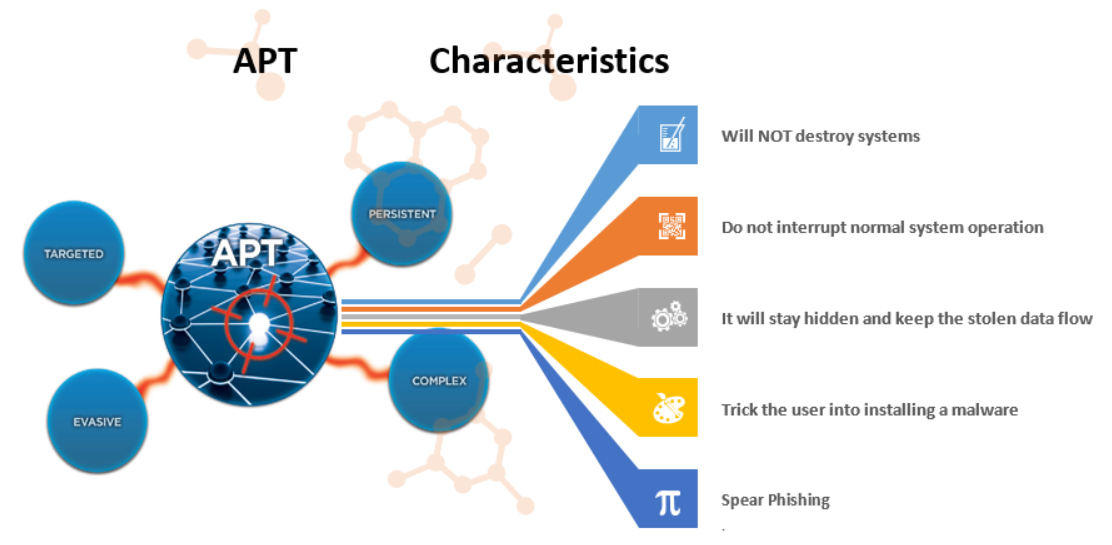
- The level of deception
- The use of multiple attack vectors (channels of attack)
- Well-researched social engineering attacks on specific, targeted individuals
- Stealthy Trojan horse attacks using malware techniques
- Well calculated to bypass contemporary security countermeasures.
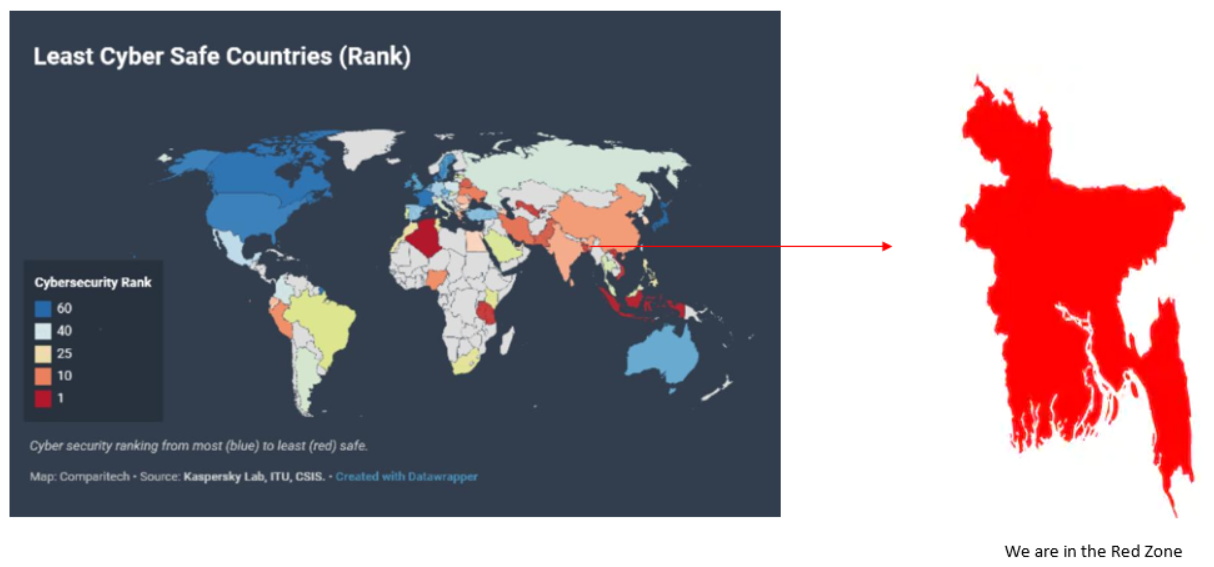
Cyber safe ranking according to Kaspersky
Where are we?
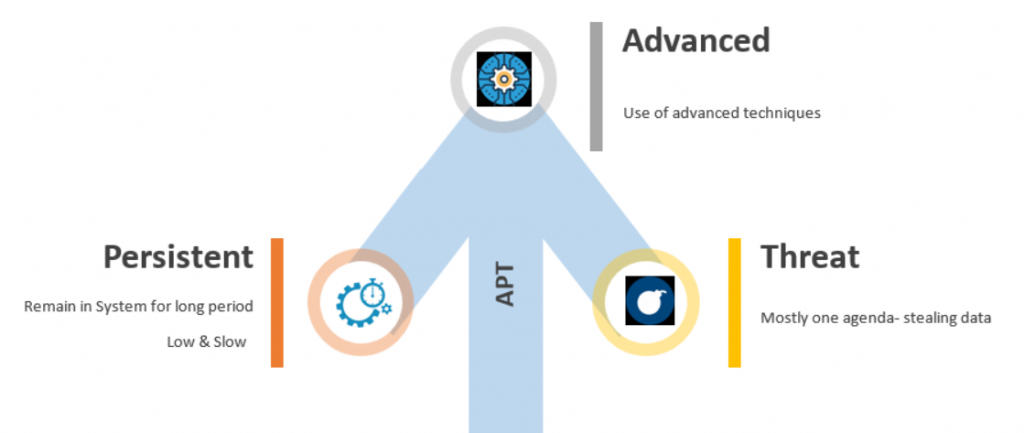
Elements of APT
Sounds simple yet can bring far reaching impacts
Most noticeable data Exfiltration
Affected user perspective -2017
| Datee | Organization | Number of Affected People | What Got Leaked |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13th July | Republican National Committee | 200 million | Names, Phone Numbers, Home Addresses, Voting Details, DOB |
| 19th June | Verizon | 14 million | Names, Phone Numbers, PINSB |
| 15th March | Dun & Bradstreet (DB) | 33.7 million | Email Addresses, Contact Information |
| 12th March | Kansas Department of Commerce | 5.5 million | Social Security Numbersn |
| 21st March | America’s Job Link Alliance (AJLA) | 4.8 million | Names, DOB, Social Security Numbers |
| 7th July | World Wrestling Entertainment (WWE) | 3 million | Names, Earnings, Ethnicity, Address, Age Range |
| 17th July | DOW Jones | 2.2 million | Names, Customer ID’s, Email Address |
| 29th July | Equifax | 143 million | Social Security Numbers, Names, Address, Drivers License |
| 1st Aug | Esports Entertainment (ESEA) | 1.5 million | Locations, Login Details, Email Addresses, DOB, Phone Numbers |
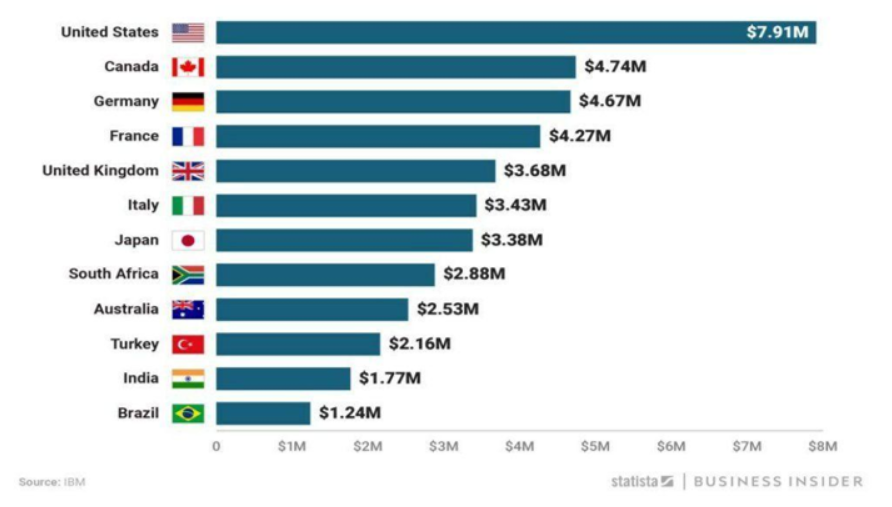
Global Data breach cost
Financial perspective-2018
APT DEMYSTIFIED
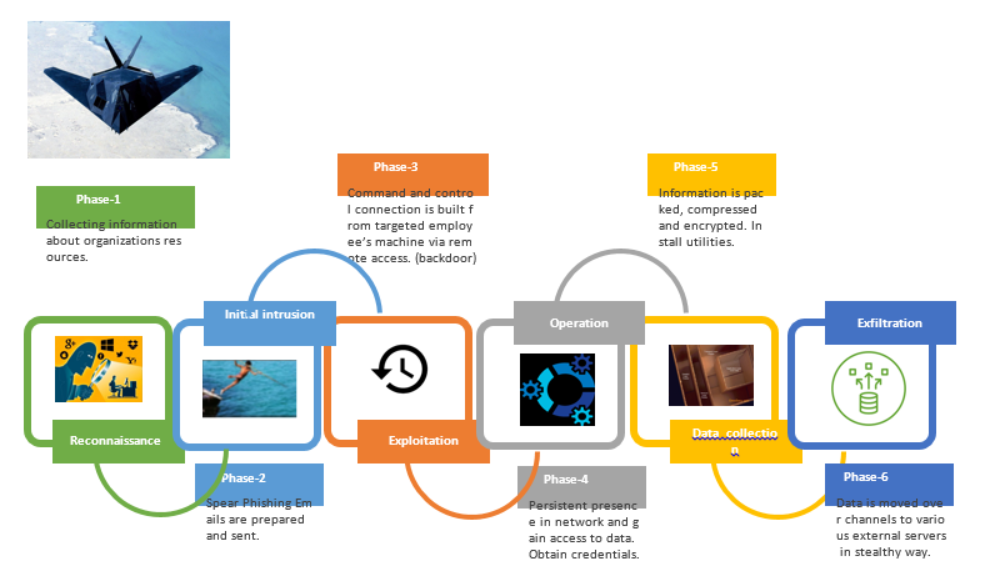
Stages of APT
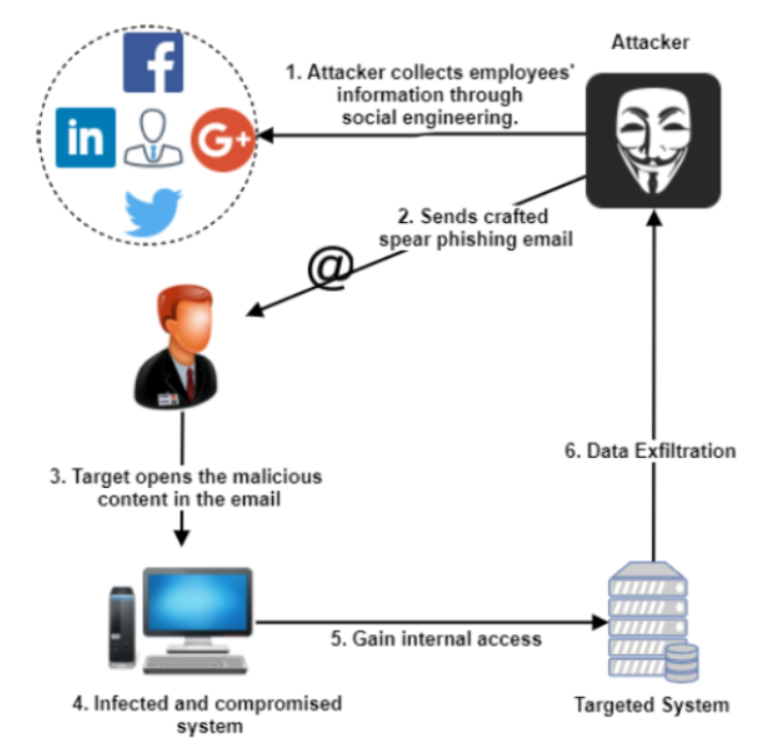
Spear Phishing vs Watering Hole
Spear Phishing
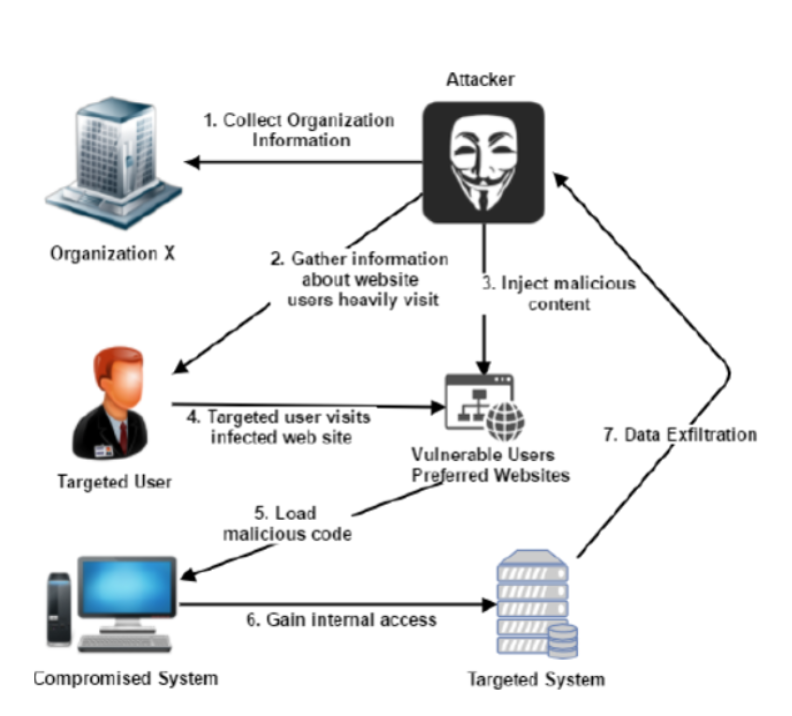
Watering Hole
More about Phishing
Enemies are finding new ways


APT ATTACK SCENARIOS
Step 1- Recon
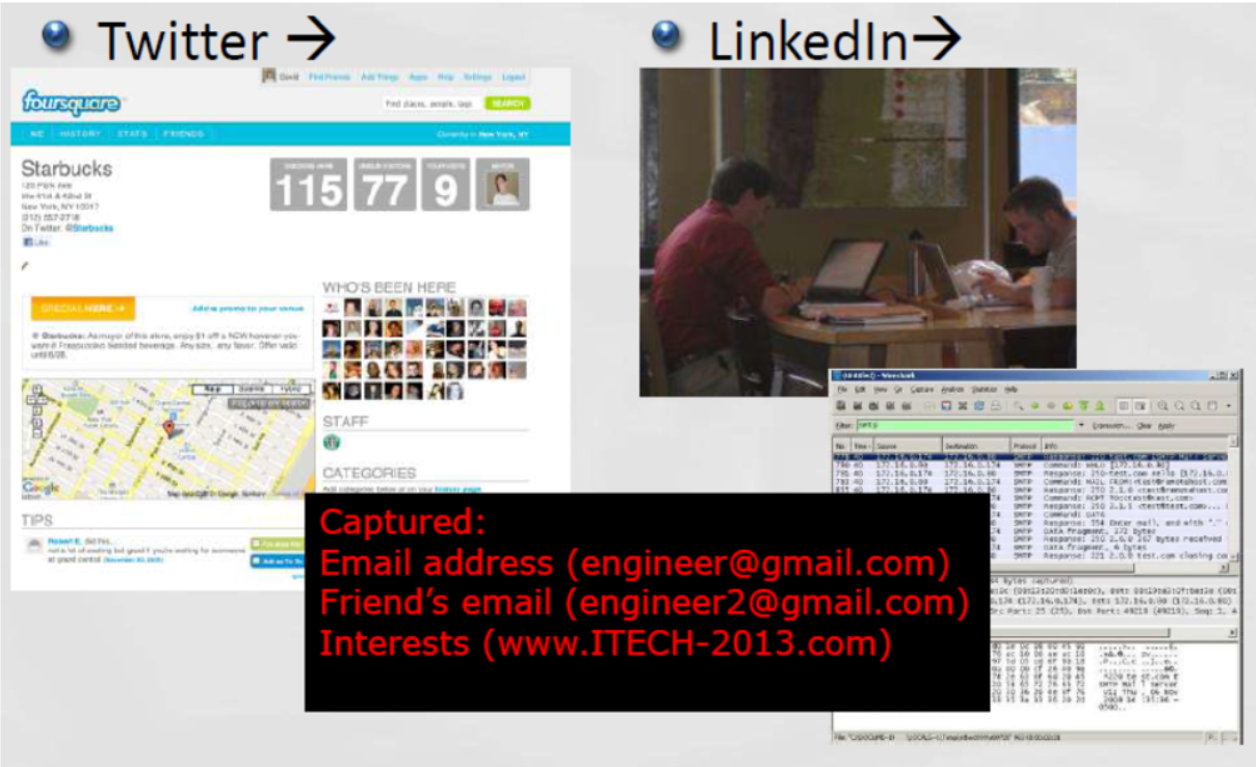
Step 2- Targeted Attack
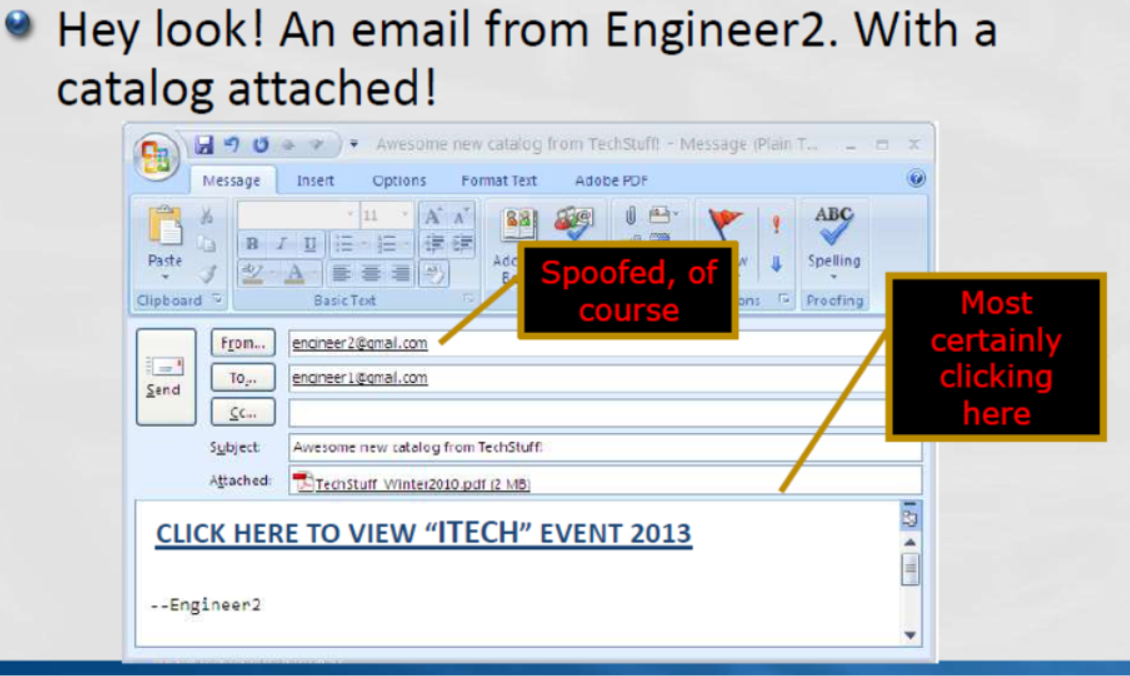
Step 3- Gaining Access
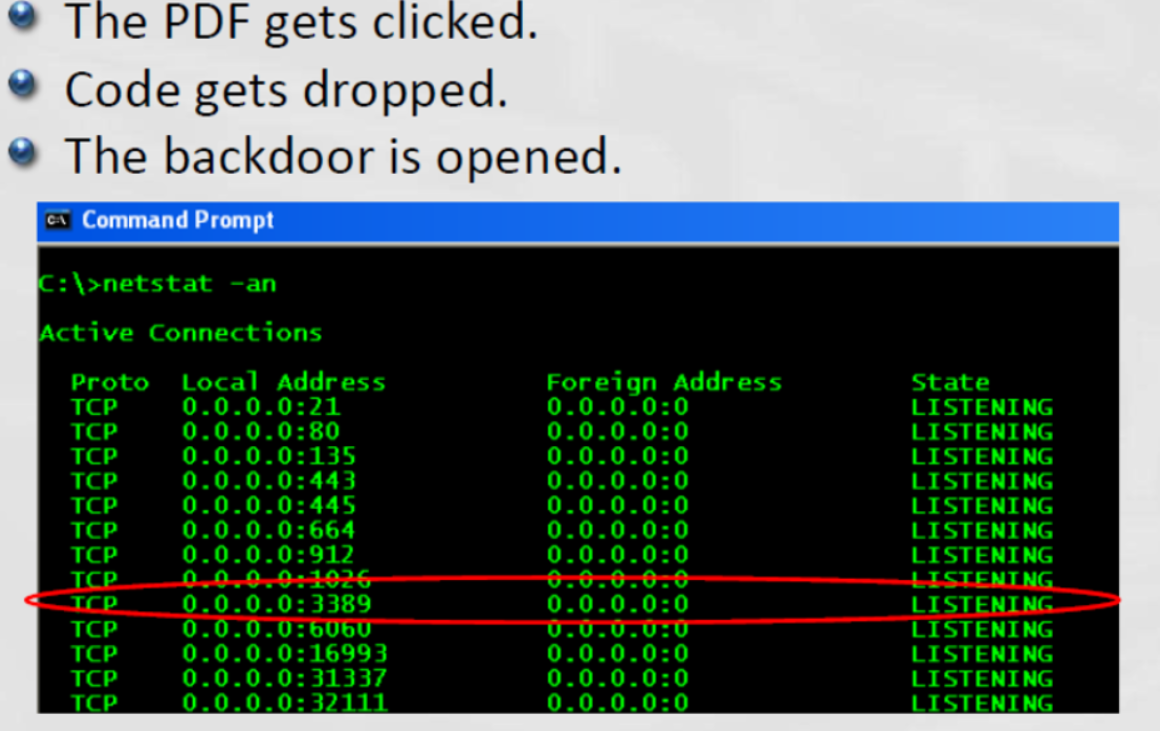
Step 4- Command & Control
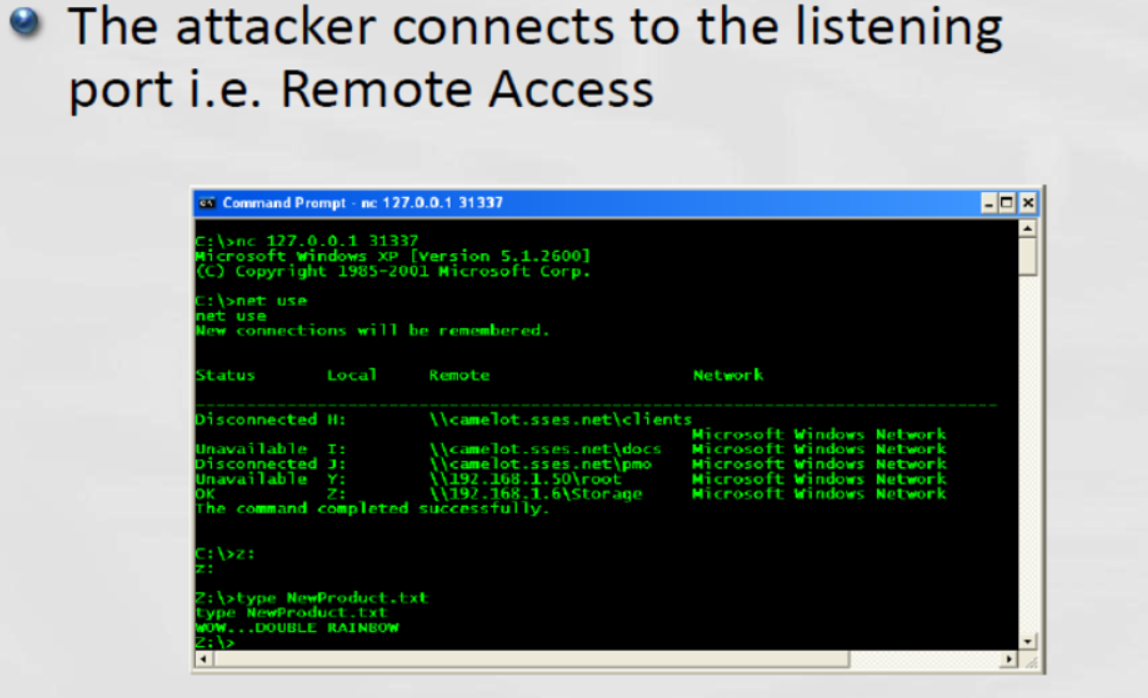
Step 5- Data Packaging

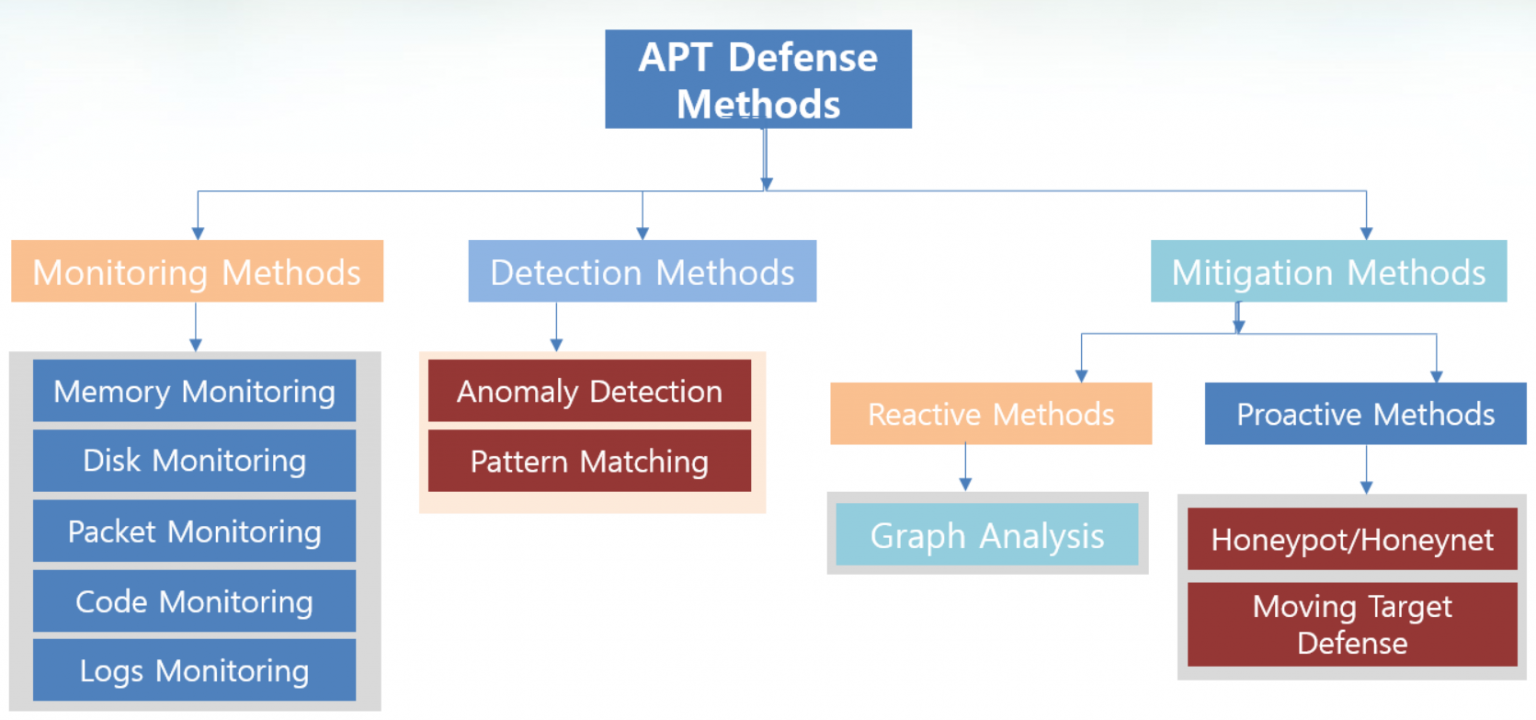
APT DEFENSE METHODS

Defending against APT
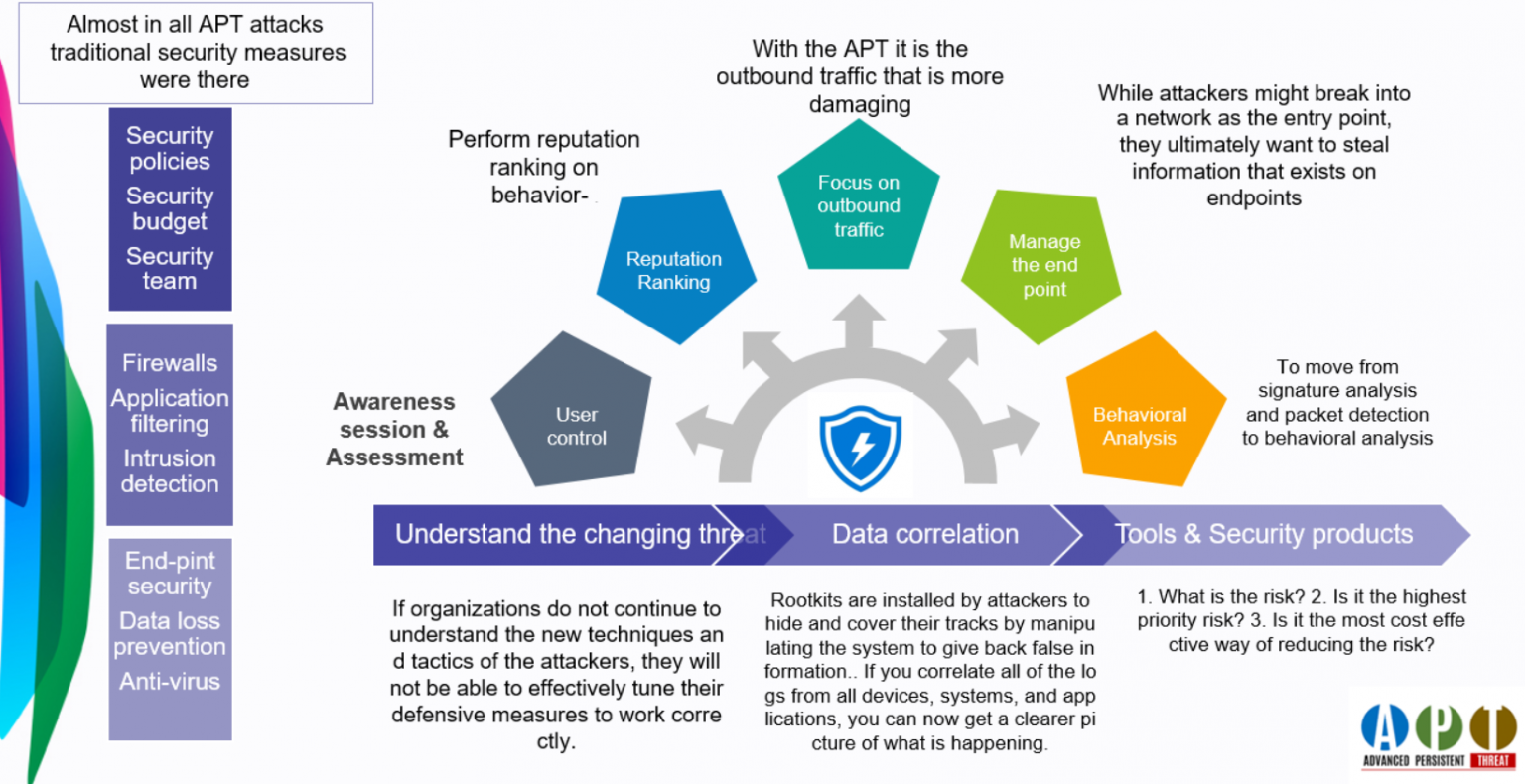
Make your hygiene right
| Develop Overview of Enterprise Infrastructure: |
| Compile a list of all DNS & DHCP Server |
| Compile a list of all internet points of presence |
| Compile a list of all VPN Connectors |
| Compile a list of all Windows Domains |
| Create a network diagram of the core network infrastructure |
| Compile the rule set of the core firewall |
| Implement Robust Logging: |
| Implement logging on all DNS servers to include queried domain name and systems performing the query to centralized logging utility |
| Implement logging on all DHCP servers to log hostname and IP address pairing and date/time information to centralized logging utility |
| Ensure Windows application, system, and security event logs are appropriately sized and logging locality |
| Ensure both success and failure audits are being logged for all systems |
| Increase the storage of key logs (such as VPN, Firewall, DNS) to ensure they are not overwritten |
| Configure anti-virus and/or host-based intrusion prevention to log to centralized logging utility |
| Implement logging on all internal web proxy servers to log date/time, hostname and IP address pairing and URL browsed information to centralized logging utility. |
| Implement logging of all traffic on all firewalls to centralized logging utility. Note that packet contents are not required. |
| Centralized the Storage and Analysis of Key Logs : |
| Integrate Key Logs (Such as firewall, VPN, DHCP, DNS, etc) into a Security Information Event Management (SIEM) solution. |
| If a SIEM is not in place, store key logs in a central location |
Combination of different methods provide ideal protection
APT assessment & stage wise defense methods
| Stages | Attack Methods | Defense Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Reconnaissance | Social Engineering | User Awareness |
| Accomplishing a foothold | Spear Phishing, Watering-Hole | Malware Inspection, Content Filtering, Blacklisting |
| Lateral Movement | Privileges Escalation, Malware, Vulnerabilities Exploitation | Access Control Listing, Firewall, Passing Control |
| Exfiltration | Command and Control | Firewall, Proxy, Encryption Use Control, Blacklisting |
| Cover Up | Traces Erasing (e.g. deleting logs) | Forensics, alerts triggered |
ML vs Statistical detection methods
| Learning Approach | Anomaly Detection Method | Source of Data | APT Stages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Supervised | Machine Learning | Network/Host Logs | Establish Foothold and Lateral Movement |
| Supervised | Machine Learning | Network Traffic | Establish Foothold |
| Semi-Supervised | Statistical | Host based logs | Accomplishing Foothold |
| Semi-Supervised | Machine Learning | Network Traffic | Accomplishing Foothold, Lateral Movement, Exfiltration |
| Supervised | Machine Learning | Malware Detection | Accomplishing Foothold |
| Supervised | Machine Learning | Network Traffic | Lateral Movement, Exfiltration |
| Supervised | Machine Learning | Network Traffic | Internal Exfiltration |
| Supervised | Machine Learning | Emails | Reconnaissance, Establishing Foothold |
| Supervised/Unsupervised | Machine Learning | Host/Network events | Not specific to a stage, stablished behavior profiling |
| Unsupervised | Machine Learning | Active directory domain service logs | Lateral Movement, Data Exfiltration |
Moving targets defense techniques
| Category | Details | MTD Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Diversity [85] | SDN- based solutions for Moving Target Defense. Network and Host MTD | OS hiding, Network Reconnaissance Protection |
| Shuffle [86] | Target Movement based on attack probability | VM migration |
| Redundancy [87] | OpenFlow based random host mutation | Physical IP mapping to corresponding virtual IP. Network MTD. |
| Shuffle [88] | Fingerprint hoping method to prevent finger print attacks. Host MTD | Game theoretic model for fingerprint hopping |
| Diversity [89] | Dynamic game based MTD for DDos Attacks. Network MTD. | Dynamic game for flooding attacks. |
| Shuffle, Diversity, Redundancy [90] | Security models for MTD. Network MTD | Effectiveness Analysis for MTD countermeasures |
| Diversity [91] | Dynamic MTD using multiple OS rotation. Host MTD | Network threat-based OS rotation |
| Shuffle [92] | Optimal MTD Strategy based on Markov game. Application MTD | Dynamic game, MTD Hopping |
| Diversity [93] | Software Diversity and Entropy Based MTD. Application MTD | Cost, Usability analysis of software diversity |
| Shuffle [94] | Software Defined Stochastic Model for MTD | High availability and MTD cost Modeling |
| Redundancy [95] | Decoy based cyber defense using Randomization. Network MTD | IP address randomization |
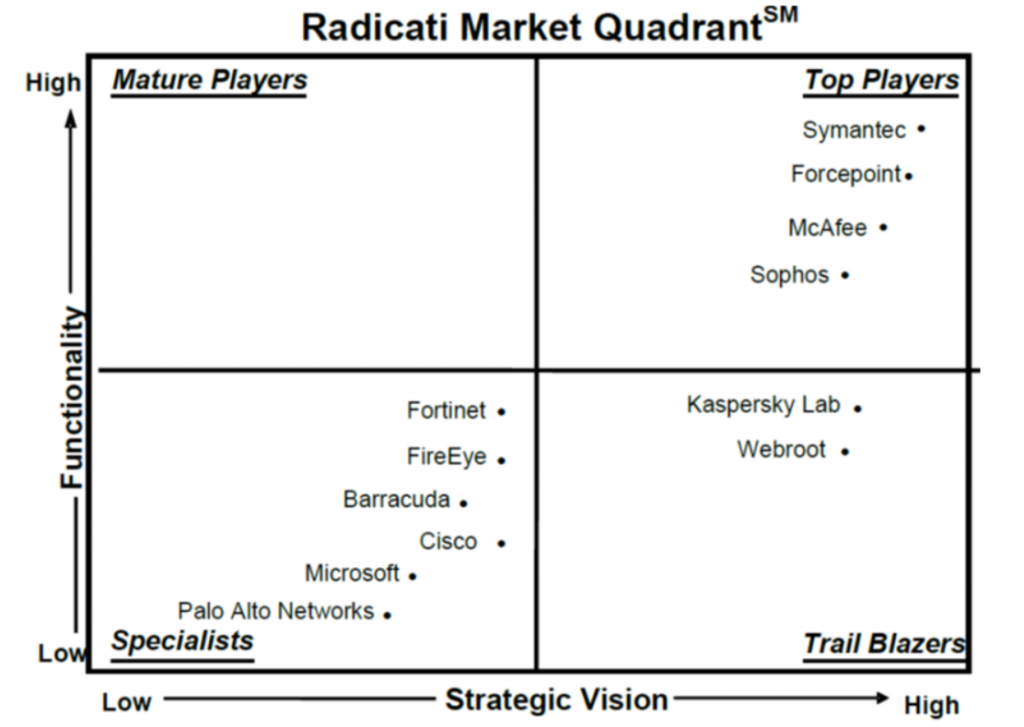
Leading APT solution providers